|
|
|
Concurrent Programming with Java
Lab Manual, Version 1.0, F. Astha Ekadiyanto,
2002.
Lab 3: Building Applets - Graphical representation
Similar to the process in defining draw(Graphics) method in the CircleCell, the declaration of HexCell Class should change into:
public class HexCell extends Cell implements Visualization
Then add a new method called draw(Graphics g) inside the Class definition.
This time we will use the drawPolygon(Polygon) method.
But, before we could call the drawPolygon(Polygon) method, we must first
create a Polygon Object that represent the HexCell Shape.
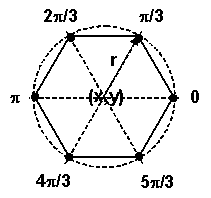
We can create a Hexagonal Polygon just by adding the six corner points into the Polygon Object. Of course, things would be easier if we could define a looping process for it.
Polygon polygon = new Polygon();
for( int i=0; i<6;i++)
{
int x1 = (int) ( x + r * Math.cos(i*Math.PI/3));
int y1 = (int) ( y + r * Math.sin(i*Math.PI/3));
polygon.addPoint(x1,y1);
}
After that, drawing Polygon should be very simple
g.drawPolygon(polygon);
The complete implementation in Java is shown below.
import java.lang.Math;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Polygon;
public class HexCell extends Cell implements Visualization
{
// . . . all other code of the original HexCell Class
public void draw(Graphics g)
{
|